Intoduction to Digital Electronics
By Stephen Bucaro
The entire field of computer technology relies on transistors. In fact, an Intel i7 microprocessor
is constructed of about 731,000,000 transistors. Transistors operate by using the special
properties of semiconductor materials. A semiconductor is a material whose ability to conduct
electricity can be controlled. The most common semiconductor is the element silicon.
Silicon and oxygen are most abundant elements on earth, most of it is combined to make silica,
the material of which most sand and rocks are made. Like all elements, a silicon atom consists
of protons and neutrons in its nucleus, and electrons arranged in shells around the nucleus.
Each shell has a propensity to hold a certain number of elections, depending upon its distance
from the nucleus. The properties of an element depend primarily on the number of electrons
in it's outermost shell.
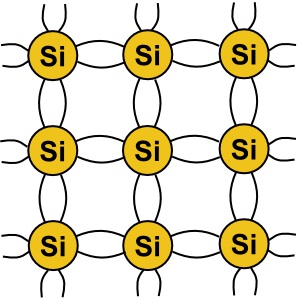
A silicon atom has three shells around its nucleus, the outermost shell holding four elections,
called "valence electrons" because they have a propensity to be shared with other atoms.
In pure form, silicon atoms will share their valence electrons causing them to arrange into
a crystal lattice. The diagram above shows how the silicon atoms share their valence electrons
to form a crystal.
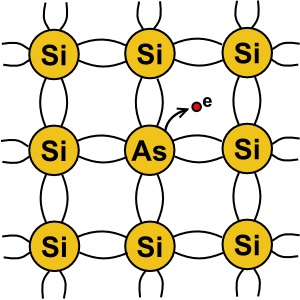
Pure silicon is actually a non-conductor. In order to make silicon into a semiconductor, atoms
of a "dopant" element must be integrated into silicon's crystal structure. One element used as
a dopant is arsenic. Arsenic has five valence electrons. So when an arsenic atom is embedded
in a silicon crystal structure, this creates free electrons. When a material has an abundance
of free electrons, it makes a good conductor.
When a dopant with an extra electron in its valence shell is used, it creates an "N type" semiconductor.
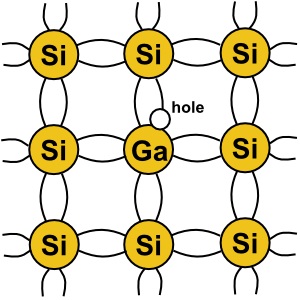
Another element used as a dopant is gallium. Gallium has three valence electrons. So when
a gallium atom is embedded in a silicon crystal, this creates a an election deficiency in the crystal
structure called a "hole". A hole leaves an excess of positive charge, which attracts elections,
making it a good conductor. When a dopant that creates holes is used, it creates a "P type"
semiconductor.
| 
